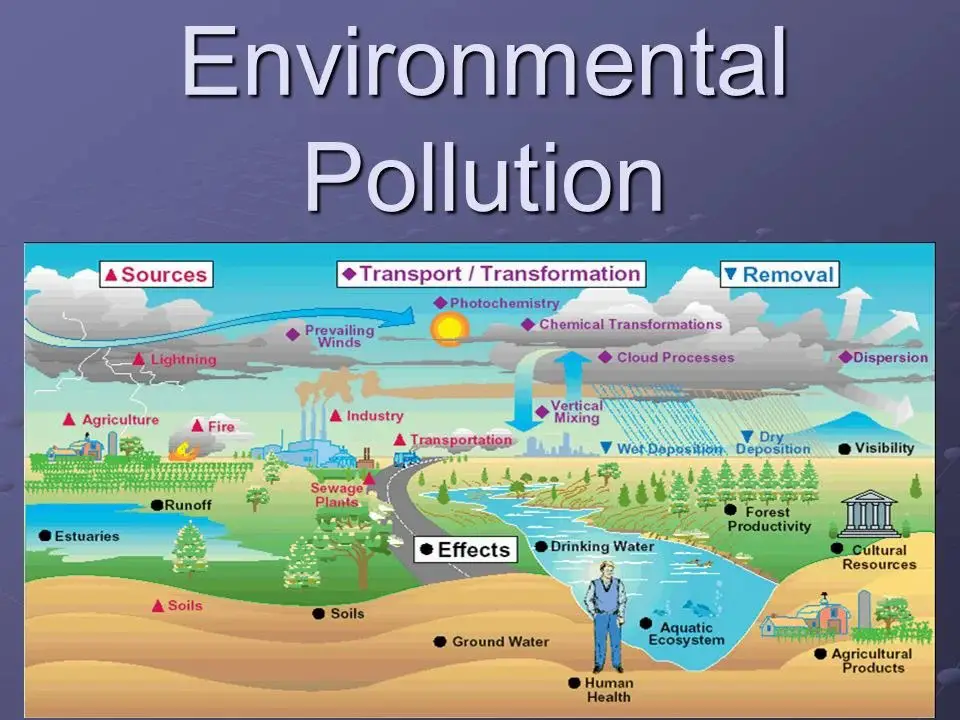
1. urbanization and industrialization
Since the era of industrial revolution, man has continued to put dangerous substances in the environment at a dangerous rate. Industrialization, urbanization, economic development and environment are associated with a combination of positive and negative effects. Generally, in many countries, urbanization and rapid economic growth occurs where the transfer of population from villages to cities and towns has been observed. One of the results of uncontrolled urbanization in developing countries is the environmental decline. This occurs very fast, resulting in excessive air pollution, water contamination, waste disposal challenges and many other problems such as barren agricultural land.
Most likely, rapid increase in industrialization, modernization and urbanization contributes to environmental pollution worldwide, but its effect is more in developing countries. Water resources are beginning to decrease, and with an increase in population, there is a possibility of any more or even drying due to indifference to water conservation and waste of water. Also, water bodies become contaminated due to pollution, so that they do not remain potable. In addition, the discharge of waste in land and water bodies is excessive due to industrialization. With rapidly growing urbanization and industrialization, huge amounts of waste water, heavy metals, toxic muds and solvent streams and rivers enter, causing them to become polluted.
Urbanization has increased the increase in automobile and motor vehicles manifold, which is a serious concern for air pollution. Finally, industrialization is promoting heavy housing destruction through cutting of trees for wood, construction of roads and construction of houses, which contribute to the destruction of all ecosystems and the extinction of some animal and plant species.
2. Mining and investigation
The process of mining and exploration produces different amounts of pollution, which affects the quality of air, water and land. The amount of pollution depends on the phase and magnitude of the work being done on the site. Excavation of the mining site alone can produce waste materials, become synchron and resulting resulting in destruction. In the process of mining of a particular valuable substance such as gold ore, other toxic elements such as lead (PB) can come out and pollute both soil and water. Although mineral exploration can cause slight pollution, soil, water, and air pollution may be more intense as a result of various stages of exploration. Pollution is even greater when it arises from large -scale exploitation of rocks, petroleum and limestone used in various construction works. In most oil -producing states in African countries, the miscreants illegally break the oil pipelines and extract oil for refining into illegal refineries. Often, these illegal refineries are burnt by security agencies with the intention of stopping bunning.
However, this burning action produces huge amounts of carbon compounds, sulfur compounds, organic pollutants and toxic metals that produce serious consequences not only for the environment but for both terrestrial and aquatic life. For example, acidic rainfall is seen, the presence of greenhouse gases increases heat intensity, and fish and other aquatic animals die in superficial water. Cement factories and mining functions in limestone mines can lead to large amounts of dust in the air, which further increase the environmental pollution.
3. Agricultural activities
Agriculture is a source of economic development for any country and maintains the livelihood of the people. Despite these important roles of agriculture, pollution still arises from agricultural activities resulting in many health and environmental risk. Agricultural pollution can begin with some agricultural activities that damage, contaminates and spoil the environment and ecosystem. A source of pollution in farming is to burn waste materials emanating from agricultural activities such as cleaning of land, using more fertilizers of plants and some such pest control chemicals that are non-casualial. These procedures include the entry of certain chemical substances in the food nets, the production of smoke and PM and unstable of the houses. In addition, nitrate groundwater emanating from agricultural processes is known as chemical pollutants in hydroelectrics. Utrophification caused by additional nutrients in water bodies is usually related to fertilizers that are planted in greater quantity for the absorption of plants. Additional nitrogen and phosphate can leak into surface water or ground water through runoff. In addition to pollution caused by farming on agricultural land, the upbringing of terrestrial or aquatic animals also pollutes the environment. For example, animal feeds or animal excreta can cause a sharp smell, which can affect health. In addition, the desire to increase the production of agricultural products for continuous growing population maintaining has promoted the use of antifoured agents, antibiotics and fungicides in farming, further increased the pollution of the ecosystem. Although agriculture is a basic need for humans and it is needed to feed the human population, pollution caused by agricultural activities should be the most concern.
4. Fossil fuel burning
Fossil fuel can emit harmful air pollutants long before burning. When fossil fuels are burnt, many air pollutants are emitted, which cause environmental pollution and destruction of ecosystems. To meet our energy requirements, we burn oil, coal and gas, and they promote the current global temperature growth crisis. Burning of fossil fuels emit a variety of primary and secondary pollutants, including airborne particles, SO2, CO2, CO, Hydrocarbons, organic compounds, chemicals and nitrogen oxides (NOX). Fossil fuel emissions include major greenhouse gases including carbon dioxide, methane (CH4), nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases. Therefore, air pollution caused by these activities not only pose a threat to air quality, but is also partially responsible for climate change and global warming.
5. Particulate matter
PM is an important component of the atmosphere. PM’s sources can be natural or man -made sources. There are many natural sources that put millions of tonnes of PM in the atmosphere. These include volcanic eruptions, wind and dust storms, forest fire, salt spraying, rock debris, gaseous emissions and soil erosion. Man-made activities such as fuel combustion, industrial processes, steel industry, petroleum foundry, cement, glass manufacturing industry, smelting and mining work, fly-ash emissions from power plant, coal burning and agricultural waste also contribute to the PM.
6. Plastic
People are beginning to understand to what extent plastic has contributed to environmental pollution. Some types of plastic found in the natural environment include polypropylene, polyethylene, polystinine, polyamide and polyester. In most developing countries, plastic bags are mainly used in purchasing and storage of foods due to their strength and cost. Also, most of the beverages sold in glass bottles are now packed in plastic bottles. However, in some places, beverages are drunk in these plastic bottles and the bottles are thrown indiscriminately, which increases the large amount of plastic in the environment. Plastic is largely non-biodigradeble, but it can be converted into macro- or microplastic.
It was reported that the growth of municipal solid waste production in the United States between 1960 and 2013 was 188%, while plastic production was 8238% (Tsiamis et al., 2018). However, the increase in plastic production occurred with a decrease in waste production from glass and metal. Mainly, microplastic (MP) consumer products such as paints, cosmetics and washed synthetic clothing are found in fiber, while secondary MPs arise from large plastic debris. Most are surface plastic MPs (0.33 4.75 mm). MP pollution has been identified as a threat to the coastal sea environment. However, research continues to clarify the environmental impacts of MP distribution, concentrations and characteristics.
Read Also:
- Major Types Of Pollution
- Environmental Pollution
- Effects Of Pollution On Aquatic Biota
- A Review On The Effects Of Water Pollution On Freshwater Fish Species
- Water Pollution: Causes, Negative Effects And Prevention Methods
- Prevention Of Water Pollution
- Effects And Control Ways of Water Pollution
- Causes Of Water Pollution
- Introduction To Air Quality And Pollution Control
- Introduction And History Of Anthropogenic Pollution
- Air Pollution And Your Health
- What Is Air Pollution
- Health Effects Of Plastic Pollution